In English, words have different jobs in sentences, and we call them “parts of speech.” There are eight main parts: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections. Nouns name things, verbs show actions, adjectives describe things, and adverbs tell us more about actions. Pronouns take the place of nouns, prepositions show relationships, conjunctions connect words; and interjections express strong feelings. Knowing these parts helps us talk and write in a way that makes sense to others.
Parts of Speech Chart
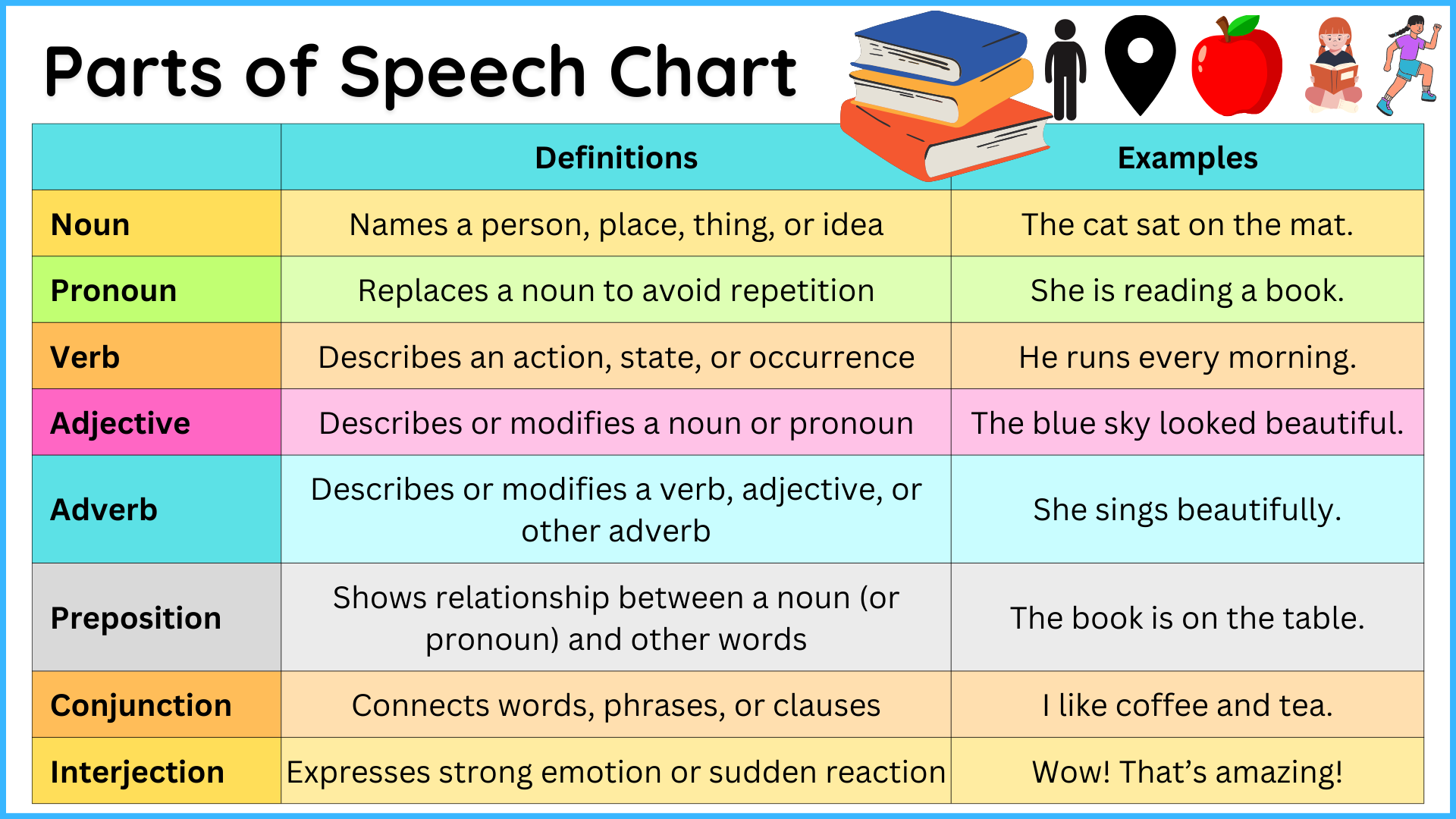
Here’s a chart of all the parts of speech with concise examples:
| Parts of Speech | Definition | Usage | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Noun | Names a person, place, thing, or idea | Subject, object | The cat sat on the mat. |
| Pronoun | Replaces a noun to avoid repetition | Substitute for a noun | She is reading a book. |
| Verb | Describes an action, state, or occurrence | Expresses what the subject does | He runs every morning. |
| Adjective | Describes or modifies a noun or pronoun | Adds details to nouns/pronouns | The blue sky looked beautiful. |
| Adverb | Describes or modifies a verb, adjective, or other adverb | Answers “how,” “when,” “where,” or “to what extent” | She sings beautifully. |
| Preposition | Shows relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and other words | Indicates location, time, or direction | The book is on the table. |
| Conjunction | Connects words, phrases, or clauses | Links ideas or elements | I like coffee and tea. |
| Interjection | Expresses strong emotion or sudden reaction | Adds emphasis or reaction | Wow! That’s amazing! |
| Article | Defines a noun as specific or unspecific | Indicates specificity | The apple is red. |
Parts of Speech in English
- Noun
- Pronoun
- Adjective
- Verb
- Adverb
- Preposition
- Conjunction
- Interjection

Noun
A noun is a word used as the name of a person, place, thing, idea, quality, state/condition/position/attitude/action.
- Person: Mary, doctor, friend
- Place: Paris, school, beach
- Thing: Car, book, computer
- Idea: Love, democracy, freedom
- Quality: Beauty, intelligence, kindness
- State/Condition/Position/Attitude: Happiness, health, manager, optimism
- Action: Running, reading, dancing
In simple terms, nouns are the names we use for people (like “teacher” or “friend”), places (such as “school” or “park”), things (like “book” or “cat”), and ideas (such as “happiness” or “freedom”). Nouns are essential building blocks in sentences, and they help us communicate about the people, objects, and concepts in our world.
Example Sentences:
- I have a cat named Whiskers.
- Let’s play at the park.
- My mom makes delicious cookies.
- The sun is shining brightly.
- School is where we learn new things.
- My toy is missing; can you help me find it?
- Pizza is my favorite dinner.
- The moon is visible at night.
- His smile brightened the room.
- The bird sings a sweet song.
- The tree has colorful leaves.
- My friend and I are going to the store.
- Books take us on adventures.
- The car goes vroom-vroom.
- Happiness is sharing with others.
- The rain makes everything fresh.
- The baby laughs when tickled.
- The dog barks loudly.
- The flower blooms in spring.
- The moon looks like a silver coin.
- My dad cooks tasty dinners.
- The house is painted blue.
- The river flows quietly.
- The clock tells us the time.
- The teacher helps us learn.
Pronoun
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun.
Instead of saying the same noun over and over, we use pronouns to make sentences shorter and less repetitive. Examples of pronouns include he, she, it, they, we, and you. So, instead of saying “Mary is happy. Mary is playing with Mary’s toys,” we can use pronouns and say “Mary is happy. She is playing with her toys.” Pronouns make talking and writing easier!
Example Sentences:
- I have a teddy bear.
- Mom gave me a cookie.
- We play hide and seek.
- Can you sing a song?
- He likes chocolate ice cream.
- She has a pretty dress.
- It is a fluffy bunny.
- They are my new classmates.
- The cat purrs when it is happy.
- You and I can be friends.
- We found a colorful ball.
- Grandma told me a bedtime story.
- He and she are siblings.
- The dog wags its tail.
- It is a yellow school bus.
- They share toys with others.
- I see a rainbow in the sky.
- You can draw a smiley face.
- She sings a lullaby.
- We love to play in the park.
- It rains on a cloudy day.
- The baby giggles happily.
- He rides a blue bicycle.
- You and I learn together.
- They have a big family.
Remember that:
First Person:
-
- Singular: I, me (e.g., I am happy. Give it to me.)
-
- Plural: We, us (e.g., We are going. It belongs to us.)
Second Person:
-
- Singular: You (e.g., You are my friend.)
-
- Plural: You (e.g., You all are invited.)
Third Person:
-
- Singular:
- He, him (e.g., He is reading. I gave it to him.)
- She, her (e.g., She is singing. I talked to her.)
- It (e.g., The cat is sleeping. It looks cozy.)
- Plural:
- They, them (e.g., They are playing. I saw them.)
- Singular:
Adjective
An adjective modifies or describes a noun or pronoun.
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun (a person, place, thing, or idea) by adding more information about its qualities or characteristics.
Adjectives help provide details and make the nouns in sentences more specific. For example, in the phrase “a blue sky,” the word “blue” is an adjective describing the quality of the sky. Adjectives can express color, size, shape, quantity, and other attributes that help give a clearer picture of the noun they modify
Example Sentences:
- I have a big teddy bear.
- The yellow sun is shining in the sky.
- She has a soft blanket.
- The tasty pizza is on the table.
- His red car is parked outside.
- The small puppy is very cute.
- We saw a funny movie yesterday.
- My mom makes the yummy cookies.
- The green grass feels cool under my feet.
- This is a heavy backpack.
- The happy child is playing in the park.
- The purple flowers are blooming.
- It was a sunny day at the beach.
- I found a shiny coin on the ground.
- The old book has interesting stories.
- Her pink dress is so pretty.
- The fast car zoomed down the road.
- We saw a quiet lake in the mountains.
- He drew a fun picture in class.
- The cold ice cream melted quickly.
- The bright stars lit up the night sky.
- The hard puzzle took a long time to solve.
- This is a new toy for you.
- The tall tree provides shade.
- The happy song made everyone smile.
Verb
A Verb is a word that expresses an action or fact.
Verbs are fundamental elements in sentences, and they convey what the subject of a sentence is doing or experiencing. For example, in the sentence “She runs every morning,” the word “runs” is a verb indicating the action the subject (she) is performing. Verbs can represent physical actions (like run, jump, eat), mental actions (like think, believe, understand), or states of being (like is, are, am). They play a crucial role in constructing sentences and giving them meaning.
Example Sentences:
- She runs in the park.
- The cat jumps on the bed.
- We eat pizza on Fridays.
- The sun shines in the sky.
- He laughs at funny jokes.
- I play with my toys.
- Dogs bark when they’re excited.
- They build a sandcastle at the beach.
- I love chocolate ice cream.
- The baby cries when hungry.
- She reads a book before bed.
- Birds fly in the air.
- We watch movies on weekends.
- He listens to music.
- Flowers bloom in the spring.
- I understand the story.
- The wind blows gently.
- She teaches math.
- They hike in the mountains.
- The clock ticks softly.
- I am happy.
Adverb
An adverb is a word that modifies or describes a verb, an adjective, or another adverb.
An adverb modifies or describes a verb, an adjective, or another adverb.
Adverbs often provide information about how, when, where, or to what degree an action is performed. They add details to a sentence, helping to convey more precise meanings. For example, in the sentence “She sings beautifully,” the word “beautifully” is an adverb that describes how she sings. Adverbs can answer questions such as how, when, where, or to what extent, enhancing the overall understanding of a statement.
Example Sentences:
- She sings beautifully.
- He runs fast.
- They arrived early for the meeting.
- I eat my dinner slowly.
- The cat climbed the tree easily.
- The sun sets quietly.
- The kids played in the park happily.
- She speaks English well.
- I will come to the party later.
- The car moves slowly in traffic.
- They completed the task easily.
- The birds chirped loudly in the morning.
- The train arrives every day at 9 AM.
- She solved the puzzle quickly.
- He reads the book carefully.
- They danced nicely on stage.
- The rain fell softly on the roof.
- The children played outside.
- I will meet you soon.
- She laughed heartily at the joke.
- The team played well in the match.
- He works hard every day.
- She answered the question correctly.
- The cat sleeps peacefully on the windowsill.
- I go to the gym regularly.
Preposition
A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and other words in a sentence.
A Preposition is a word which is put before a noun or pronoun in order to show some relation between them.
Prepositions often indicate location, direction, time, or the relationship between different elements in a sentence. Common prepositions include words like “in,” “on,” “under,” “over,” “beside,” “between,” and “among.” For example, in the sentence “The book is on the table,” the word “on” is a preposition indicating the location of the book in relation to the table. Prepositions are essential for providing context and helping to clarify the spatial and temporal relationships in language.
Example Sentences:
- The cat is under the chair.
- She walked in the garden.
- The ball is between two friends.
- They sat beside the tree.
- The airplane flew above the clouds.
- The book is on the desk.
- The school is near the park.
- He jumped over the puddle.
- The cat sleeps on the bed.
- They live in the house.
- The sun sets behind the mountains.
- The dog ran around the yard.
- She is hiding behind the door.
- The keys are in the bag.
- The river flows through the valley.
- We walked along the path.
- The ball rolled under the table.
- The bird flew across the sky.
- They met at the park.
- The children played among the trees.
- The cat jumped onto the chair.
- The school is next to the library.
- The car is parked in front of the house.
- The airplane landed on the runway.
- The treasure is buried beneath the sand.
Conjunction
A conjunction joins words, phrases, or clauses.
Conjunctions are used to join and coordinate elements to express relationships between them. Common conjunctions include words like “and,” “but,” “or,” “because,” and “if.” For example, in the sentence “I like tea and coffee,” the word “and” is a conjunction that connects the two beverage choices. Conjunctions play a crucial role in forming coherent and structured sentences by linking related ideas, actions, or thoughts.
Example Sentences:
- I like apples and bananas.
- She wants pizza or pasta for dinner.
- He ran fast but he didn’t win.
- I’ll play outside if it’s sunny.
- We can go to the park or the beach.
- The cat is small but cute.
- I’ll read a book and then go to bed.
- You can have ice cream or cake.
- I’ll call you when I’m ready.
- He is happy but tired.
- You can draw or color the picture.
- She is good at singing and dancing.
- I have a cat and a dog.
- He can swim but not dive.
- You can play now or later.
- I want tea or coffee.
- The sun is hot, so wear sunscreen.
- It’s raining but we can still go out.
- You can wear the blue shirt or the red one.
- I’ll come to the party if I’m not busy.
Interjection
Interjections are often standalone words that convey feelings like surprise, joy, excitement, or pain. They can also express agreement, disagreement, or greeting. Interjections are typically followed by an exclamation mark or a comma, and they serve to add emotion or emphasis to a sentence. Examples of interjections include “Wow!,” “Ouch!,” “Oh no!,” and “Hey!”
Example Sentences:
- Wow! That’s a big balloon.
- Yay! We’re going to the zoo.
- Oops! I spilled some milk.
- Ouch! That hurt my toe.
- Hey! Look at that bird.
- Hooray! It’s your birthday!
- Oh no! I forgot my umbrella.
- Aww! The kitten is so tiny.
- Phew! That was a close call.
- Yikes! I didn’t see that coming.
- Oops! I made a little mistake.
- Well! Let’s try again.
- Gee! That was a fast car.
- Hello! How’s your day going?
- Bravo! You did great!
- Alas! I missed the bus.
- Ugh! This puzzle is tricky.
- Hurray! It’s the weekend!
- Oh dear! I broke my toy.
- Hmm! What should I wear?
- Oops! I tripped on a shoelace.
- Hey! Can I borrow your pen?
- Well! That’s interesting news.
- Aww! The baby is laughing.
- Yikes! That was a loud noise.
Quiz:
- What is a word used as the name of a person, place, thing, or idea?
- a) Verb
- b) Noun
- Which word describes or modifies a noun by giving more information about its qualities?
- a) Adverb
- b) Adjective
- What is a word that takes the place of a noun in a sentence?
- a) Pronoun
- b) Conjunction
- Which word connects words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence?
- a) Verb
- b) Conjunction
- What expresses strong emotions, sudden exclamations, or brief remarks?
- a) Interjection
- b) Noun
- Which word shows the relationship between a noun and other words in a sentence?
- a) Adverb
- b) Preposition
- What word expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being?
- a) Verb
- b) Adjective
- Which word is used to join and coordinate elements in a sentence?
- a) Adjective
- b) Conjunction
- What is a word that modifies or describes a verb, an adjective, or another adverb?
- a) Pronoun
- b) Adverb
- What is a word that connects words or groups of words in a sentence?
- a) Interjection
- b) Preposition
- Which word is used to express a strong feeling or sudden emotion?
- a) Adjective
- b) Interjection
- What is a word that shows the relationship between a noun and its surroundings?
- a) Pronoun
- b) Preposition
- Which word is used to indicate time, place, or direction?
- a) Adjective
- b) Preposition
- What is a word that shows a relationship between a noun and a pronoun?
- a) Conjunction
- b) Preposition
- Which word is used to introduce a clause and show a relationship between ideas?
- a) Adverb
- b) Conjunction
Answers:
- b) Noun
- b) Adjective
- a) Pronoun
- b) Conjunction
- a) Interjection
- b) Preposition
- a) Verb
- b) Conjunction
- b) Adverb
- b) Preposition
- a) Adjective
- b) Preposition
- b) Preposition
- b) Preposition
- b) Conjunction